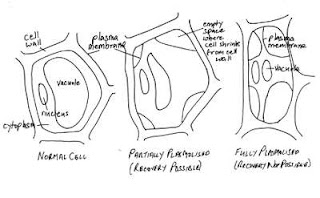
 The far left diagram shows a normal cell in a hypotonic solution. After placing in hypertonic salt solution, plasmolysis begins. In its early stages (central photo (sorry, not to scale)), wilting occurs which, in the early stages is reversible by placing plant in plain water. However, as plasmolysis progresses, the cytoplasm shrinks so much that it often causes the roots to shrink also. This stage is fatal - there is no recovery potential.
The far left diagram shows a normal cell in a hypotonic solution. After placing in hypertonic salt solution, plasmolysis begins. In its early stages (central photo (sorry, not to scale)), wilting occurs which, in the early stages is reversible by placing plant in plain water. However, as plasmolysis progresses, the cytoplasm shrinks so much that it often causes the roots to shrink also. This stage is fatal - there is no recovery potential.Note: we also saw this condtion over winter when we looked at cell freezing.
No comments:
Post a Comment